
When embarking on a home improvement project, one of the critical decisions homeowners face is the choice of materials. Heat-Treated Glass is emerging as a highly preferred option due to its unique combination of aesthetic appeal and practical advantages. This specialized type of glass undergoes a heating and cooling process that significantly enhances its strength and durability compared to standard glass. As a result, it becomes an ideal solution for a variety of applications, ranging from windows and doors to shower enclosures and glass partitions.
The benefits of using Heat-Treated Glass extend beyond mere aesthetics. Its impressive resistance to thermal stress makes it a safer choice for homes, reducing the risk of breakage and ensuring longevity. Homeowners can achieve sleek, modern designs without compromising safety, which is why Heat-Treated Glass is increasingly favored in contemporary architecture. By opting for this versatile material, individuals can elevate the elegance of their living spaces while simultaneously enhancing functionality and value. As such, incorporating Heat-Treated Glass in your next home improvement project is not just a trend but a smart investment in both beauty and safety.

Heat-treated glass, also known as tempered glass, has become a popular choice for homeowners looking to enhance both the aesthetic and functional aspects of their spaces. One of the primary benefits of heat-treated glass is its superior strength. According to industry studies, it can withstand up to five times the impact of standard glass, making it an ideal option for areas prone to accidents or extreme weather conditions. This durability contributes to safety, as tempered glass shatters into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, significantly reducing the risk of injury.
In addition to its strength, heat-treated glass also offers enhanced thermal resistance. It can tolerate rapid temperature changes, which is essential for environments that experience wide fluctuations in temperature. A report from the Glass Association highlights that the use of heat-treated glass can lead to improved energy efficiency in homes, helping to regulate indoor temperatures and potentially lowering energy costs. As homeowners increasingly focus on energy efficiency, this aspect makes heat-treated glass a smart investment.
Tips: When selecting heat-treated glass for your home improvement project, ensure you choose the appropriate thickness for your specific application. Additionally, consider incorporating low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings for better insulation properties. Always work with a certified professional to ensure that the installation adheres to local building codes and safety standards.
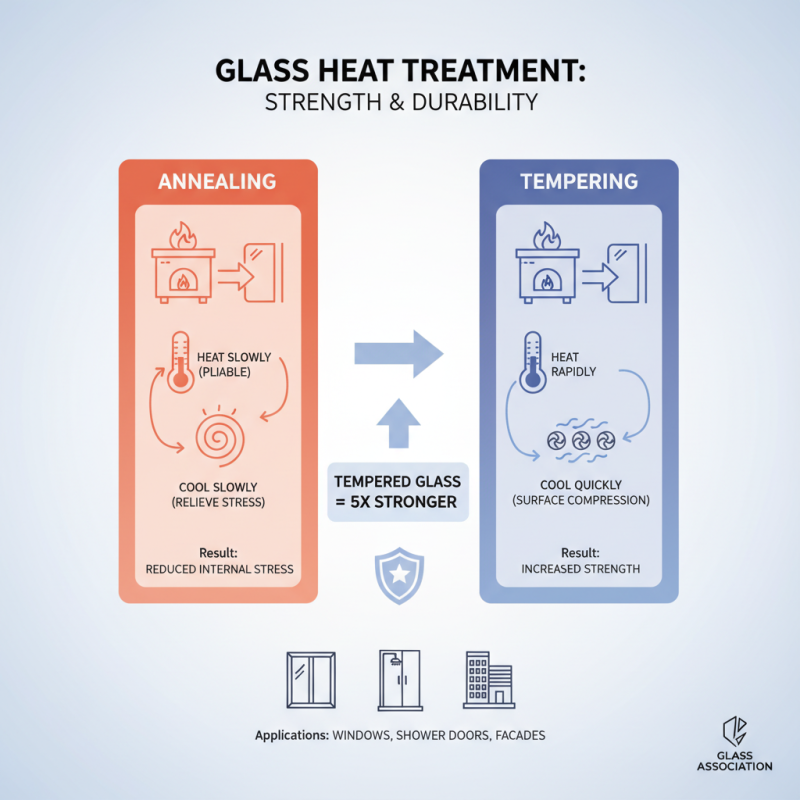
The heat treatment process for glass involves subjecting the material to high temperatures and controlled cooling, enhancing its strength and durability significantly. This process typically includes two main techniques: annealing and tempering. During annealing, glass is heated to a temperature where it becomes pliable, then cooled slowly to relieve internal stresses. In contrast, tempering involves rapidly heating the glass and quickly cooling it, creating a surface compression layer that improves its load-bearing capacity. According to the Glass Association, tempered glass can be up to five times stronger than standard glass, making it an ideal choice for various applications, including windows, shower doors, and glass facades.
The benefits of heat-treated glass are evident not only in its structural integrity but also in its safety features. In the event of breakage, tempered glass shatters into small, blunt pieces, reducing the risk of injury—an essential quality for installations in homes where safety is a top priority. Industry reports suggest that using heat-treated glass can reduce the likelihood of glass-related accidents by over 30%. Furthermore, heat treatment can enhance the thermal resistance of glass, allowing it to withstand significant temperature fluctuations without risk of cracking, a key consideration for energy-efficient home designs. Overall, understanding the heat treatment process reveals why it is a crucial element in modern home improvement projects.
When considering materials for home improvement projects, heat-treated glass emerges as a superior choice compared to standard glass options. Regular glass is more susceptible to breakage, posing safety risks, especially in high-traffic areas or regions prone to extreme weather. In contrast, heat-treated glass undergoes a special tempering process that enhances its strength, making it much less likely to shatter upon impact. This resilience is essential for both interior and exterior applications, where durability is a top priority.
Additionally, heat-treated glass offers better thermal resistance. It can withstand higher temperatures, which is especially beneficial in spaces with fluctuating climates or near heat sources like fireplaces. Regular glass may warp or crack under stress, but heat-treated variants maintain their structural integrity. This property not only ensures a safer living environment but also minimizes the need for frequent replacements, ultimately proving to be a cost-effective long-term investment. The aesthetic appeal of heat-treated glass, with options for various finishes and tints, also makes it a versatile choice for any home design.
Heat-treated glass, also known as tempered glass, has gained popularity in residential settings due to its enhanced strength and safety features. According to the Glass Association, tempered glass is four to five times stronger than standard glass, making it an ideal choice for areas prone to high impact and thermal stress. This durability makes it suitable for applications such as shower doors, windows, and glass railings, where safety is paramount. The ability to withstand high temperatures also makes it a preferred material for glass cooktops and fireplace doors, contributing to both aesthetics and functionality in modern homes.
In addition to its strength and thermal properties, heat-treated glass offers significant design flexibility. Its ability to be custom cut and finished allows homeowners to use it in a variety of ways. The National Glass Association reports that the use of large-format tempered glass in facades and sliding doors enhances natural light while maintaining structural integrity. This not only improves energy efficiency but also complements contemporary design trends that emphasize open spaces and seamless indoor-outdoor transitions. The rising trend of using glass in home improvement projects underscores the material's versatility and its growing acceptance among homeowners seeking elegant and practical solutions.
Heat-treated glass is a popular choice for home improvement projects due to its remarkable safety features and durability. Unlike standard glass, heat-treated glass undergoes a specialized process that increases its strength by undergoing controlled heating and cooling. This treatment allows the glass to withstand significant impacts, making it less likely to break under stress. In the event of breakage, heat-treated glass shatters into small, blunt pieces, minimizing the risk of injury and making it a safer option for homes, especially in areas with high traffic or where children play.
Another significant advantage of heat-treated glass is its impressive thermal resistance. It can endure extreme temperature fluctuations without warping or cracking, ensuring that windows and doors maintain their integrity across varying climates. This durability not only protects the glass itself but also enhances energy efficiency in the home by reducing thermal transfer. As a result, projects incorporating heat-treated glass can lead to lower heating and cooling costs, providing long-term benefits for homeowners. With these safety features and exceptional durability, heat-treated glass is an ideal material for enhancing both the functionality and aesthetic appeal of any home improvement project.
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Safety | Heat-treated glass is designed to withstand high stress and impact. | Reduces the risk of injury in case of breakage, creating a safer home environment. |
| Durability | Manufactured to be stronger and more resilient than regular glass. | Longer lifespan, reducing the need for replacement and repairs. |
| Thermal Resistance | Can endure extreme temperature fluctuations without cracking. | Ideal for climates with significant temperature changes, maintaining structural integrity. |
| Design Flexibility | Available in various shapes and sizes, customizable for any project. | Enhances aesthetics while providing functional benefits. |
| Energy Efficiency | Can be treated to reflect heat, improving insulation. | Reduces energy costs by maintaining indoor temperatures. |





